Are Gymnasts Smarter?
Does gymnastics lead to academic achievement? Yes.
And I’ll tell you why.
Gymnastics actually makes the brain stronger, fitter and more ready and willing to learn!
Gymnastics is good for your children’s school work.
There’s an inextricable relationship between physical activity, cognitive development and academic achievement.
This article will explore this relationship by looking at-
- The mind/body connection- how the areas of the brain that co ordinate gymnastics movements also organise the flow of information
- How learning new and challenging gymnastics movement patterns makes your brain grow stronger!
- How gymnastics aerobic activity optimises your brain function
- How physical fitness leads to academic achievement
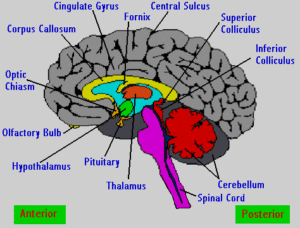
1. Mind/ Body Connection- Gymnastics, the Brain and Organising Information:
This is straight forward biology.
If you’re not particularly interested in the details of how the cerebellum, pre frontal cortex, hippocampus or basal ganglia works- and how they are stimulated with gymnastics exercises – skip this section.
All you really need to know is….
The basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex are major players in physical activity and thinking and
The areas of the brain that control physical movement like in gymnastics – also coordinate the flow of information.
Here’s How…..
Cerebellum:
The cerebellum (with help from the motor cortex and basal ganglia)
- Coordinates physical movement and the movement of thoughts. They order the steps for a physical movement and those necessary for cognitive operations. Just as the cerebellum orders the movement necessary toperform a forward roll in gymnastics, it helps sequence the thoughts necessary to visualize a room in your house, make a persuasive argument or think up a song.
- The cerebellum also coordinates attention, emotions and even social skills.
- The cerebellum is a primitive part of the brain that is hard at work when we learn how to do something physical. It makes up about 10% of the brain’s volume and contains half of our neurons.
- It keeps rhythm for more than just motor activity and regulates certain brain systems so they run smoothly.
- Finally, the cerebellum is highly involved with the integration of information and the rate at which information is processed, all essential to thinking, learning and memory.
The Pre Frontal Cortex (works closely with the hippocampus and motor cortex)
- The prefrontal cortex organizes mental and physical activity.
- It is like the CEO of the brain performing such acts as overseeing working memory, inhibiting stimuli, initiating action, judging, planning and predicting.
The brain circuits used to order, sequence, and time a physical act are the same ones used to order, sequence, and time a mental act.
The entire front half of the brain is devoted to organizing mental and physical action (e.g., working memory, motor planning, the ability to inhibit competing stimuli, thoughts, and action).
And in gymnastics classes, we also reinforce this continually.
When we ask kids in gymnastics lessons to “wait and leave enough following distance before your turn” – we are not only being safe- but also asking gymnasts to plan and judge when it’s ok to initiate action.
When we require gymnasts to start specifically with their left leg [or right leg], combine 3 or 4 movements together in a sequence, do their gymnastics movements on the mats (not on the floor)- again we are asking them to use their working memory, organise their physical (and mental actions), use spatial skills and judgement as well as plan their gymnastics movements.[Motor skills]
When we ask them to concentrate on the teachers instructions instead of their friend’s joke- we are asking them to inhibit competing stimuli.
In fact in our Gym Wizards gymnastics classes we have a rule “we don’t touch each other in the line”- which helps kids keep their hands to themselves while awaiting their turns- preventing distractions.
When we ask them to put their hands on one gymnastics mat (e.g the red mat) and land on another gymnastics mat (e.g the blue mat)- we are asking gymnasts brains to plan, organise, judge, memorize and execute an action.
I can see the steam coming out of their little ears sometimes!!
Basal Ganglia
- Physical and mental processes that have been mastered are stored in and executed from the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum in the lower brain.
So when your kids have mastered a cartwheel- and I ask them to do it at gymnastics classes, they use their brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum in the lower brain to execute the movement.
Complex or new physical actions or cognitive processes are managed further up in the brain, toward the frontal cortex.
When your kid is learning a front somersault at gymnastics- or any new gymnastic movement for that matter- they startusing their “upper brain”- near the frontal cortex.
2. How New Gymnastics Movements Makes Your Brain Grow Stronger!
In physical education and gymnastics lessons, kids regularly do moderate to vigorous physical activity and practice new and challenging gymnastics movement patterns. [skills]
These aspects of gymnastics education make the brain better equipped to learn.
The key aspects are
1. that the movement pattern [gymnastics skill] must be challenging to the child and
2. gymnastics movements are accompanied by feedback that tells the gymnast what and how to improve.
When we learn how to perform a gymnastic movement pattern that requires us to think deeply about what the body will do, how it will move, where it will move and with whom or what they body will move with (e.g, gymnastics movements like cartwheels, a backward roll or a handstand) – we are exercising the same areas of the brain that are involved in all of the cognitive functions used throughout the school day.
Complex physical activities [especially like those in gymnastics- like a handstand, cartwheel or somersault] put all the brain systems to use by strengthening and expanding neural networks.
The more complex the bodily movements the more complex the resulting synaptic connections become.
These circuits are used by other areas of the brain for various types of thinking.
For example, in gymnastics warm ups to music, moving to an irregular rhythm versus a steady, regular rhythm improves brain plasticity (the flexibility or adaptability of the brain).
The brain grows stronger in much the same way muscles do through resistance training.
When gymnasts are learning a new motor skill, the circuits linking the cerebellum, basal ganglia and prefrontal cortex get going and their performance improves.
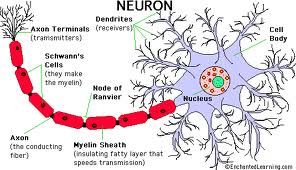
While practicing these types of gymnastics motor skills we create thicker myelin around nerve fibres.
This improves the quality and speed of the signals and the efficiency of brain circuitry.
Practicing an activity such as running and hurdling onto a springboard or mini trampoline from one foot onto two- and then performing a jump with different shapes in the air (e.g a star jump)-requires the mastering and coordination of many bodily movements.
When children learn to develop such gymnastics movements they experience an increase in academic abilities such as memory retrieval and cognitive abilities.
This is because physical and mental tasks require the same neurons to be shared increasing the likelihood of long term learning.
Complex physical activities and aerobic activity – like those performed at gymnastics lessons -have distinct positive and complementary effects on the brain.
3. How Aerobic Gymnastic Activity Optimises Your Brain Function
Regular physical activity is the single most important tool you have to optimize your brain function.
Aerobic gymnastics activity elevates neural transmitters, creates new blood vessels that send growth factors and spawns new cells. Aerobic gymnastics activity also improves executive function and moves more blood and nutrients into the brain.
Aerobic gymnastics activity augments the number and density of blood vessels in the motor cortex and cerebellum.
In short- gymnastics exercise helps the brain become more fit.
The more we move and stress our body, the better our circulation is and the more fit our brain becomes. Gymnastics exercise produces stronger, healthier and happier brains.
The product of regular gymnastics physical activity is physical fitness.
Gymnastics classes for kids are partly made up of aerobic exercises (like during the pulse raising activities and games in the warm up) and partly skill development (mastering new skills)
4. How Gymnastics Leads To Academic Achievement
The human capacity to think, plan and learn is rooted in the parts of the brain that govern movement.
Physical activity- like gymnastics- cues the building blocks of learning in the brain.
Physical activity also affects mood, anxiety, and attention, guards against stress and reverses some of the effects of aging in the brain.
Gymnastics exercise has a profound effect on cognitive abilities.
Physical activity creates an environment in which the brain is ready, willing and able to learn.
How?
- The brain responds like muscles do, growing with use and shrivelling with inactivity.
- Neurons in the brain connect to each other like leaves on branches. Physical activity at gymmastics causes these branches to grow and bloom with new buds, enhancing brain function.
- Physical activity like at gymnastics influences learning directly, at a cellular level, improving the brain’s potential to store and process new information.
Interestingly, only creatures that move have a brain.
That which we call thinking is the evolutionary internalization of movement.
As our species evolved our physical skills have developed into abstract abilities to predict, sequence, estimate, plan, rehearse, observe ourselves, judge, correct mistakes, change tactics, and remember everything we did in order to survive.
Your body was designed to be physically challenged.
When you push your body at gymnastics you challenge your brain as well. Learning and memory have evolved together with the motor functions.
As far as you brain is concerned if you are not moving there’s no real need to learn anything.
Conclusion: Gymnastics Physical Activity Helps Kids Learn on Three Levels:
1. It optimizes alertness, attention, and motivation.
2. It prepares and encourages nerve cells to bind to one another, which is the cellular basis for storing new information.
3. It spurs the development of new cells from stem cells in the hippocampus.
I think its fair to say that gymnasts make smarter kids!